Ineffective Breathing Pattern - Ineffective Airway Clearance - Impaired Gas Exchange
Nursing Care Plan for Guillain-Barre Syndrome
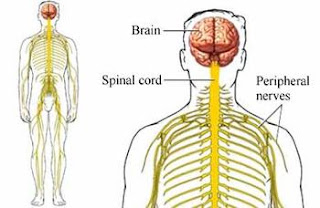
Guillain-Barre syndrome is a severe inflammatory disorder of the peripheral nerves. It is an autoimmune disease, i.e. the immune system that is supposed to attack foreign substances like bacteria; starts attacking cells of own body, in this case the nerves. The immune system produces special molecules, called the antibodies that are mainly responsible for damage to nerve cells in Guillain-Barre Syndrome. A previously healthy person suddenly develops tingling and numbness primarily in the feet which within a couple of weeks spreads through the body to cause loss of muscle control and feeling throughout the body.
Symptoms of Guillain-Barre syndrome :
- Lack of feeling
- Weakness or itchiness in arms or legs
- Possible loss of feeling and movement in the upper body, face, arms and legs.
Diagnosis
Gullain Barre syndrome is considered to be the most harmful disorder because it attacks the patient suddenly and surprisingly. The patient within weeks reaches the highest level of weakness. In 3rd or 4th weeks of the illness the patients are at their weakest. The recovery period can be varying according to the condition of the patient. It can be few weeks or in some cases a few years.
Nursin g Interventions for Guillain-Barre Syndrome
Ineffective Breathing Pattern, Ineffective Airway Clearance, Impaired Gas Exchange related to respiratory muscle weakness or paralysis, decreased cough reflex, immobilization.
Ineffective Breathing Pattern Definition : The exchange of air inspiration and / or expiration inadequate.
Ineffective Airway Clearance Definition: Inability to clear secretions or obstructions from the respiratory tract to maintain airway patency.
Impaired Gas Exchange Definition : Circumstances where an individual has decreased course of gas (O2 and CO2) that an actual or risk of lung alveoli and the vascular system.
Expected outcomes:
- Optimal breathing.
- Normal breath sounds.
- Patent airway.
- Blood gas analysis values within normal limits.
1. Monitor the number of respiratory rhythm and depth every 1-4 hours.
R /: Paralysis of breathing can occur 48 hours.
2. Auscultation of breath sounds every every 4 hours.
R /: breath sounds indicate inadequate ventilation.
3. Maintain effective airway, suction and clean the mouth.
R /: a patent airway.
4. Help the patient to cough effectively.
R /: Increase effective airway.
5. Perform chest physiotherapy.
R /: Preventing pneumonia and atelectasis.
6. Collaboration in the provision of oxygenation.
R /: Fulfilling the need of oxygen.
7. Monitor blood gas analysis.
R /: Knowing the changes in oxygen in the blood.
8. Assess the level of consciousness and skin tone.
R /: Changes in blood gas analysis will affect the level of consciousness and skin tone.
ads
0 komentar: